| Research Article | ||
Open Vet. J.. 2025; 15(1): 300-306 Open Veterinary Journal, (2024), Vol. 15(1): 300-306 Research Article Detection of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, IndonesiaNaomi Lan Noviana Thesia1, Aswin Rafif Khairullah2, Mustofa Helmi Effendi3*, Wiwiek Tyasningsih4, Yulianna Puspitasari4, Susmitha Nur Ahadini1, Ikechukwu Benjamin Moses5, Sheila Marty Yanestria6, Katty Hendriana Priscilia Riwu7, Wasito Wasito2, Zein Ahmad Baihaqi8 and Riza Zainuddin Ahmad21Master Program of Veterinary Science and Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia 2Research Center for Veterinary Science, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), Bogor, Indonesia 3Division of Veterinary Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia 4Division of Veterinary Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia 5Department of Applied Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Ebonyi State University, Abakaliki, Nigeria 6Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Wijaya Kusuma Surabaya, Surabaya, Indonesia 7Department of Veterinary Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Pendidikan Mandalika, Mataram, Indonesia 8Research Center for Animal Husbandry, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), Bogor, Indonesia *Corresponding Author: Mustofa Helmi Effendi. Division of Veterinary Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia. Email: mhelmieffendi [at] gmail.com Submitted: 09/10/2024 Accepted: 13/12/2024 Published: 31/01/2025 © 2025 Open Veterinary Journal
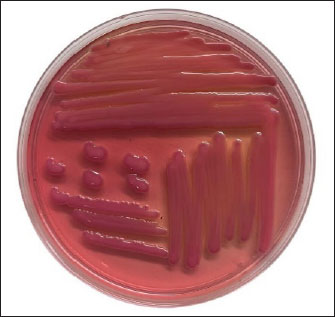
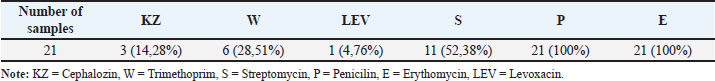
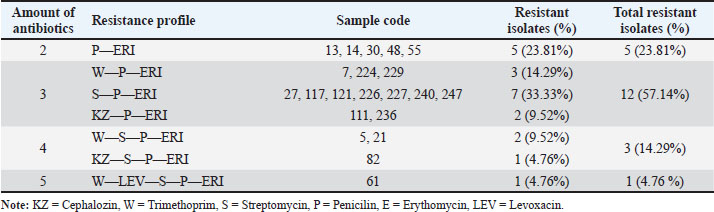
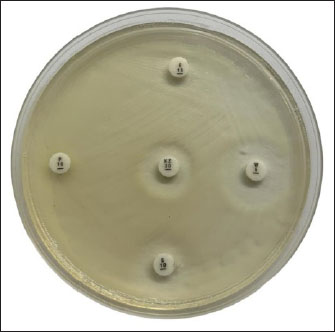
AbstractBackground: Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria is one of the pathogens that are often found in poultry and can cause various diseases in animals and humans. Currently, there are many reports of increasing multidrug resistance (MDR) K. pneumoniae showing including carbapenems, extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL), and fluoroquinolones. Aim: The purpose of this study was to determine the antibiotic resistance pattern and the presence of multidrug resistance K. pneumoniae isolates isolated from duck cloacal swabs taken from duck farms in three different sub-districts, namely Paras sub-district, Karang Turi sub-district, and Tembelang sub-district, Jombang district. Methods: This study used 180 duck cloaca swab samples and analyzed for the presence of K. pneumoniae using standard microbiology techniques. Positive isolates of K. pneumoniae were then tested for antibiotic resistance using the disk diffusion test method. Results: This study showed that 21 (100%) isolates were resistant to antibiotics and 16 (76.19%) isolates were MDR. Conclusion: The presence of bacteria that are resistant to many types of antibiotics is a threat to public and animal health. Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae, MDR, ESBL, duck, Antibiotics, Public health. IntroductionFood is a vital need for human survival. Food sources can come from livestock or plants and serve as a source of energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals (Comerford et al., 2021). Food ingredients derived from livestock can be meat, milk, and eggs (Tyasningsih et al., 2022). The need for food from livestock, especially meat, continues to increase (Henchion et al., 2021). The Indonesian Institute of Sciences/LIPI (elaborate) reported that in 2010 meat consumption was 6.95 kg/capita/year. Compared to the normal nutritional target recommended by the 2004 Food and Nutrition Works Department of 10.3 kg/capita per year, meat consumption has only reached 67.48%. Efforts to fulfill meat needs include optimizing the use of local livestock resource potential as well as diversifying various types of meat-producing poultry, one of which comes from ducks (Alders et al., 2018). In Indonesia, ducks are one of the poultry that are widely kept by lower middle class people in rural areas. This is because ducks have many benefits and are not complicated to keep. This statement is also supported by the opinion of Prayudi et al. (2023) that ducks were the first livestock to be cultivated as a source of income. The main problem in livestock farming is the decline in production caused by bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections (Rodarte et al., 2023). Diseases caused by bacteria can spread from livestock to humans in a variety of ways, including through food contamination (Rahman et al., 2020). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States report that each year, antibiotic-resistant bacteria cause around 2.8 million infections and 35,000 deaths. A large number of these germs are derived from cattle (CDC, 2019). Ducks and other poultry are often carriers of bacteria such as Salmonella and Campylobacter if contaminated and consumed by humans (Yanestria et al., 2024; Fanissa et al., 2022). In addition, several strains of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae were also confirmed to carry genes resistant to certain antibiotics (Effendi et al., 2018; Wibisono et al., 2021; Yanestria et al., 2022). Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria is one of the pathogens often found in poultry and can cause various diseases in animals and humans (Franklin-Alming et al., 2021). Some strains of this bacteria have been found to carry the blaTEM gene, which encodes the production of extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) enzymes. These enzymes can hydrolyze beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillins and cephalosporins, making the bacteria resistant to these antibiotics (Akpaka et al., 2021). Currently, there are many reports of increasing K. pneumoniae showing multidrug resistance (MDR) including carbapenems, ESBL, and fluoroquinolones (Riwu et al., 2022a). There have been numerous case reports of human deaths worldwide resulting from antibiotic-resistant K. pneumoniae infections (Walsh et al., 2023). The presence of K. pneumoniae which is resistant to antibiotics and can produce ESBL with the blaTEM gene in ducks is quite worrying and can have an impact on public health. Based on the conceptual framework above, it is expected that the results of this study can be scientific information for the community and can increase public awareness of biosecurity around the residence which is one of the goals of veterinary public health. Materials and MethodsEthical approvalThe Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia’s ethical clearance committee helped secure consent for the use of animals in research (Ethics no: 1.KEH.073.05.2024). SamplingA sample of 180 duck cloacal swabs was taken from duck farms in three different sub-districts, namely Paras sub-district, Karang Turi sub-district, and Tembelang sub-district, Jombang district. Fecal samples were taken using sterile swab sticks aseptically, then the feces were placed in a test tube containing 2% Buffer pepton water and labeled. After the samples were taken, the samples were stored in a cooler box in an upright position and taken to the laboratory. Isolation and identification of K. pneumoniaeSamples were planted on macConkey agar (MCA) media by streaking and incubated at 37°C for 18–24 hours. Furthermore, observations were made on bacterial colonies growing on MCA media including the shape, color, and edges of the colonies on the media. Typical colonies of K. pneumoniae on MCA media are mucoid pink (Riwu et al., 2022b). Identification of cell morphology using gram staining. After that, the isolate was continued with a biochemical test using the sulfide indole motility (SIM) test to test for indole, sulfide, and bacterial movement. The MR-VP test and citrate test used Simmon’s Citrate Agar. Antibiotic suceptibility testingAntibiotic resistance test was conducted using the Kirby-Bauer agar diffusion method. The antibiotics used were antibiotics that had been packaged in disc form. The clear zones formed in this test were divided into 3 categories, namely sensitive (S), intermediate (I), and resistant (R). Klebsiella pneumoniae bacterial isolates were taken in 1–2 colonies using an ose and then inserted into physiological NaCl which had been tested for turbidity with the Mc Farland 0.5 standard then 0.2 ml was taken and then gently rubbed on the entire surface of the Mueller Hinton Agar media. The sensitivity test was conducted using 6 antibiotics, namely Penicillin 10 μg, Levoxacin 10 μg, Erithomycin 10 μg, Streptomycin 10 μg, Trimethoprim 10 μg, and Cephalozin 10 μg. The media that had been inoculated with K. pneumoniae was incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. ResultBased on 180 duck cloaca swab samples taken from duck farms in Jombang Regency which were isolated on Mac Conkey Agar media, the results showed 21 positive isolates of Klebsiella pneumoiae bacteria. Klebsiella pneumoniae colonies have smooth characteristics, convex surfaces, mucoid, and pink in color. The image of K. pneumoniae isolates on MCA media can be seen in Figure 1. Further testing of K. pneumoniae bacteria using the IMViC test consisting of the Indole test, Methyl Red test, Voges Proskauer test, and Citrate test. The indole test was carried out by inoculating bacteria suspected of being K. pneumoniae on SIM media and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C. Klebsiella pneumoniae showed non-motile bacteria, could not produce H2S gas, and did not form an indole ring after the media was dripped with Kovac’s reagent. In the MR-VP test, K. pneumoniae showed negative methyl red test results indicated by no color change in the media after being dripped with methyl red reagent and positive results in the Voges Proskauer test indicated by a change in the color of the media to red after being dripped with reagents in the form of 40% KOH and alpha-naphtol. Furthermore, K. pneumoniae showed positive results in the citrate test, indicated by a change in the color of the media to blue. The results of the biochemical test can be seen in Figure 2. Isolates that showed positive results for K. pneumoniae were continued with antibiotic sensitivity testing using the disk diffusion test method with sensitive, intermediate, and resistant assessments. The antibiotic sensitivity test used six types of antibiotics from different groups, namely cephalozin, trimethoprim, levoxacin, streptomycin, penicillin, and erythomycin. The diameter of the inhibition zone was calculated from the distance of the closest cone to the antibiotic disk. Multidrug resistance assessment in bacteria is if the bacteria are resistant to three or more types of antibiotics. The antibiotic resistance pattern of K. pneumoniae isolates can be seen in Figure 2. The results of the antibiotic sensitivity test on 21 positive K. pneumoniae isolates to several types of antibiotics using the disk diffusion test method showed that 21 (100%) isolates were resistant to antibiotics and 16 (76.19%) isolates were multidrug resistant because they were resistant to three or more types of antibiotics. The results of the K. pneumoniae antibiotic sensitivity test can be seen in Table 1 and 2, and Figure 3 and 4.
Fig. 1. Presumptive K. pneumoniae colonies on Mac Conkey Agar media are mucoid and pale pink in color.
Fig. 2. Positive result of K. pneumonia in IMViC test. From left to right: voges Proskauer media; Simmon Citrate Agar Media, Methyl Red Media, Sulfide indole motility media. DiscussionThe existence of a bacterial growth inhibition zone surrounding the antibiotic disk characterizes the outcomes of tests for antibiotic resistance conducted using the Kirby Bauer method. This study showed that 76.2% (16/21) samples were MDR to chepalozin (KZ), trimethoprim (W), levoxacin (LEV), streptomycin (S), penicillin (P), and erythromycin (E). Duck farming is an important initial stage in the duck meat supply chain and the use of antibiotics are used to control pathogens in livestock. Excessive use of antibiotics can facilitate the evolution of multidrug-resistance strains (Khairullah et al., 2019). Duck droppings are also a potential reservoir for antibiotic resistance genes. Therefore, duck farming can play an important role in the production and spread of MDR strains (Prayudi et al., 2023). Longer treatment times and more challenging cures are caused by numerous reports of rising K. pneumoniae multidrug resistance, which includes resistance to carbapenems, ESBL, and fluoroquinolones (Li et al., 2023). Humans and livestock-derived Enterobactericeae may serve as a reservoir for the propagation of antibiotic resistance. A study conducted by Xu et al. (2024) stated that 186 out of 215 (86.51) Enterobactericeae strains isolated from duck farms in Zhejiang were multidrug resistant. The bacteria showed resistance to tetracycline, oxacycline, amoxicillin, trimethoprim, and chloramphenicol. Most of these six antibiotics are categorized as “critically important antimicrobials” for humans (Scott et al., 2019). Klebsiella pneumoniae has a high level of resistance to cefazolin, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, cefuroxime, and cefepime. Resistance to these antibiotics comes from water which is a shared resource between wild animals, pets, livestock, and humans. Additional research has also shown that common areas like soil and water are crucial for the spread of antibiotic resistance (Iramiot et al., 2020). Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in this study were resistant to the antibiotics cephalozin, trimethoprim, Levoxacin, Strepromycin, Penicillin, and Erythomycin. Permatasari et al. (2020) reported that K. pneumoniae isolated from chicken farms in Blitas district showed multidrug resistance to ampicillin 75%, erythromycin 42.86%, Erythromycin 42.86%, Tetracycline 35.72%, Sulfamethoxazole 32.14%, and Streptomycin 21.4%. Klebsiella spp. are naturally sensitive or moderate to penicillin, all aminoglycosides, cotrimoxazole, tetracyclines, quinolones, chloramphenicol, trimethoprim, and nitrofurantoin tested (Patilaya et al., 2019). Table 1. Percentage of K. pneumoniae antibiotic sensitivity test results.
Table 2. Klebsiella pneumoniae sensitivity test results.
Fig. 3. Antibiotic susceptibility results for K. pneumonia. KZ: Cephalozin, W: Trimethoprim, S: Streptomycin, P: Penicillin, E: Erythomycin. Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates also showed resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics (Streptomycin). This resistance can be associated with the effectiveness of Streptomycin use in the treatment of animals and humans in Indonesia. According to Siahaan et al. (2022), good treatment is the administration of a combination of Penicillin and Streptomycin antibiotics, but it is necessary to supervise the use of Streptomycin antibiotics in the treatment of animal diseases in Indonesia. In this study, K. pneumoniae bacteria also showed resistance to beta lactam antibiotics such as penicillin and cephalozin. This is in accordance with the study reported by Lee et al. (2021) which stated that K. pneumoniae isolated from pets showed 40% resistance to beta lactam antibiotics including cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and aminoglycosides. Klebsiella pneumoniae is known as a pathogen that can be carried along with food such as fresh vegetables, meat, and street food. In recent years, numerous foodborne outbreaks attributed to Klebsiella pneumoniae have been reported in multiple nations (Saha et al., 2023). The presence of bacteria that are resistant to many types of antibiotics is a threat to public and animal health. The presence of bacteria, especially K. pneumoniae, can complicate the choice of treatment for bacterial infections in both humans and animals. Veterinary policies and supervision are important to be implemented in the treatment of diseases and livestock in Indonesia. Based on this phenomena, it is imperative that all parties play a part in the One Health concept to stop the spread of MDR from getting worse. A strategy called One Health explores the connection between environmental, animal, and human health (Trinh et al., 2018). Human health is closely related to animal and environmental health. Three guiding concepts underpin the One Health approach: cooperation, coordination, and communication among the environment, animal welfare, human health, and other areas (Yopa et al., 2023). No single organization or sector is able to solve the problem alone but requires cooperation and collaboration from all sectors. It is anticipated that both human and animal health parties will implement good hygiene and sanitation in the surrounding environment and that, as human/animal health experts authorized to carry out treatment actions, they will use antibiotics more wisely to prevent the further spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
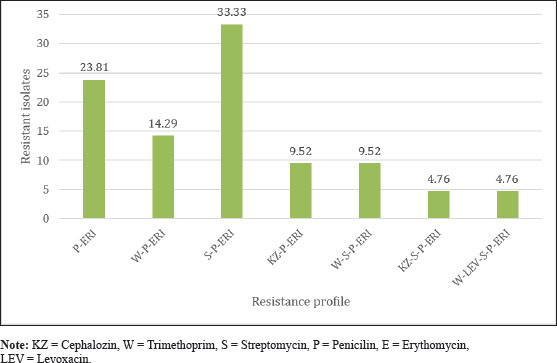
Fig. 4. Diagram of K. pneumoniae resistance profile. ConclusionKlebsiella pneumoniae was found in duck cloacal swabs taken from duck farms in three different sub-districts, namely Paras sub-district, Karang Turi sub-district, and Tembelang sub-district, Jombang district, as many as 100% (21/21) samples (100%) isolates were resistant to antibiotics and 76.19% (16/21) isolates were multidrug resistant. This study showed that 76.2% (16/21) samples were MDR to chepalozin, trimethoprim, levoxacin, streptomycin, penicillin, and erythomycin. The presence of bacteria that are resistant to many types of antibiotics is a threat to public and animal health. Veterinary policies and supervision are important to implement in the treatment of diseases and livestock in Indonesia. AcknowledgmentsThis study was done to fulfill the requirements for Degree in Master of Science in Veterinary Disease and Veterinary Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universitas Airlangga. Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. FundingThis study was partly supported by The International Research Consortium, Lembaga Penelitian dan Pengabdian Masyarakat, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia in the year 2024 with grant number: 171/UN3.LPPM/PT.01.03/2024. Author’s contributionsNLNT and WT: Conceptualization and design. WW, SNA, and ZAB: Acquisition of data. MHE and IBM: Formal analysis and interpretation of data. ARK and YP: Writing-original draft preparation. SMY, RZA, and KHPR: Writing-review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. Data availabilityAll data are available in the manuscript. ReferencesAkpaka, P.E., Vaillant, A., Wilson, C. and Jayaratne, P. 2021. Extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) produced by gram-negative bacteria in Trinidad and Tobago. Int. J. Microbiol. 2021(1), 5582755. Alders, R.G., Dumas, S.E., Rukambile, E., Magoke, G., Maulaga, W., Jong, J. and Costa, R. 2018. Family poultry: multiple roles, systems, challenges, and options for sustainable contributions to household nutrition security through a planetary health lens. Matern. Child Nutr. 14(Suppl 3), e12668. CDC. 2019. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. Atlanta, Georgia, United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/threatsreport/2019-ar-threats-report-508.pdf. Accessed on August 15, 2024. Comerford, K.B., Miller, G.D., Kapsak, W.R. and Brown, K.A. 2021. The complementary roles for plant-source and animal-source foods in sustainable healthy diets. Nutrients 13(10), 3469. Effendi, M.H., Bintari, I.G., Aksoro, E.B. and Hermawan. I.P. 2018. Detection of blaTEM Gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from swab of food- producing animals in East Java. Trop. Anim. Sci. J. 41(3), 174–178. Fanissa, F., Effendi, M.H., Tyasningsih, W. and Ugbo, E.N. 2022. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella species from chicken meat sold at Surabaya Traditional Markets, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 23(6), 2823–2829. Franklin-Alming, F.V., Kaspersen, H., Hetland, M.A.K., Bakksjø, R.J., Nesse, L.L., Leangapichart, T., Löhr, I.H., Telke, A.A. and Sunde, M. 2021. Exploring Klebsiella pneumoniae in healthy poultry reveals high genetic diversity, good biofilm-forming abilities and higher prevalence in Turkeys than broilers. Front. Microbiol. 12(1), 725414. Henchion, M., Moloney, A.P., Hyland, J., Zimmermann, J. and McCarthy, S. 2021. Review: trends for meat, milk and egg consumption for the next decades and the role played by livestock systems in the global production of proteins. Animal 15(Suppl 1), 100287. Iramiot, J.S., Kajumbula, H., Bazira, J., Kansiime, C. and Asiimwe, B.B. 2020. Antimicrobial resistance at the human-animal interface in the Pastoralist Communities of Kasese District, South Western Uganda. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 14737. Khairullah, A.R., Rahardjo, D., Rahmahani, J., Tyasningsih, W. and Harijani, N. 2019. Antibiotics resistant at Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus sp isolated from bovine mastitis in Karangploso, East Java, Indonesia. Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 13(4), 439–444. Lee, D., Oh, J.Y., Sum, S. and Park, H.M. 2021. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella species isolated from clinically ill companion animals. J. Vet. Sci. 22(2), e17. Li, Y., Kumar, S., Zhang, L., Wu, H. and Wu, H. 2023. Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Open Med. (Wars). 18(1), 20230707. Patilaya, P., Husori, D.I. and Marhafanny, L. 2019. Susceptibility of Klebsiella Pneumoniae isolated from Pus specimens of post-surgery patients in Medan, Indonesia to selected antibiotics. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 7(22), 3861–3864. Permatasari, D.A., Witaningrum, A.M., Wibisono, F.J. and Effendi, M.H. 2020. Detection and prevalence of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strain isolated from poultry farms in Blitar, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 21(10), 4642–4647. Prayudi, S.K.A., Effendi, M.H., Lukiswanto, B.S., Az Zah-Ra, R.L., Benjamin, M.I., Kurniawan, S.C., Khairullah, A.R., Silaen, O.S.M., Lisnanti, E.F., Baihaqi, Z.A., Widodo, A. and Riwu, K.H.P. (2023). Detection of Genes on Escherichia coli producing extended spectrum β-lactamase isolated from the small intestine of ducks in traditional markets Surabaya City, Indonesia. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 13(8), 1600–1608. Rahman, M.T., Sobur, M.A., Islam, M.S., Ievy, S., Hossain, M.J., El Zowalaty, M.E., Rahman, A.T. and Ashour, H.M. 2020. Zoonotic diseases: etiology, impact, and control. Microorganisms 8(9), 1405. Riwu, K.H.P., Effendi, M.H., Rantam, F.A., Khairullah, A.R. and Widodo, A. 2022a. A review: virulence factors of Klebsiella pneumonia as emerging infection on the food chain, Vet. World 15(9), 2172–2179. Riwu, K.H.P., Rantam, F.A., Effendi, M.H., Khairullah, A.R., Widodo, A., Kurniawan, S.C. and Ugbo, E.N. 2022b. Molecular detection of extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from wild deer. Biodiversitas 23(8), 4256–4262. Rodarte, K.A., Fair, J.M., Bett, B.K., Kerfua, S.D., Fasina, F.O. and Bartlow, A.W. 2023. A scoping review of zoonotic parasites and pathogens associated with abattoirs in Eastern Africa and recommendations for abattoirs as disease surveillance sites. Front. Public Health 11(1), 1194964. Saha, O., Basri, R., Hossain, M.A. and Sultana, M. 2023. Characterization of multidrug and heavy metal resistance of carbapenemases producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from poultry samples in Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 9(4), 1685–1701. Scott, H.M., Acuff, G., Bergeron, G., Bourassa, M.W., Gill, J., Graham, D.W., Kahn, L.H., Morley, P.S., Salois, M.J., Simjee, S. and Singer, R.S. 2019. Critically important antibiotics: criteria and approaches for measuring and reducing their use in food animal agriculture. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 1441(1), 8–16. Siahaan, S., Herman, M.J. and Fitri, N. 2022. Antimicrobial resistance situation in Indonesia: a challenge of multisector and global coordination. J. Trop. Med. 2022(1), 2783300. Trinh, P., Zaneveld, J.R., Safranek, S. and Rabinowitz, P.M. 2018. One Health Relationships Between Human, Animal, and Environmental Microbiomes: A Mini-Review. Front. Public Health 6(1), 235. Tyasningsih, W., Ramandinianto, S.C., Ansharieta, R., Witaningrum, A.M., Permatasari, D.A., Wardhana, D.K., Effendi, M.H. and Ugbo, E.N. 2022. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli isolated from raw milk in East Java, Indonesia. Vet. World 15(8), 2021–2028. Walsh, T.R., Gales, A.C., Laxminarayan, R. and Dodd, P.C. 2023. Antimicrobial resistance: addressing a global threat to humanity. PLoS Med. 20(7), e1004264. Wibisono, F.J., Sumiarto, B., Untari, T., Effendi, M.H., Permatasari, D.A. and Witaningrum, A.M. 2021. Molecular identification of ctx gene of extended spectrum betalactamases (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli on layer chicken in Blitar, Indonesia. J. Anim. Plant. Sci. 31(4), 954–959. Xu, D., Yan, J., Qian, M., Wang, P., Zaeim, D., Han, J. and Qu, D. 2024. Mobile genetic elements facilitate the transmission of antibiotic resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae from duck farms. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 13(2), 729–735. Yanestria, S.M., Dameanti, F.N.A.E.P., Musayannah, B.G., Pratama, J.W.A., Witaningrum, A.M., Effendi, M.H. and Ugbo, E.N. 2022. Antibiotic resistance pattern of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli isolated from broiler farm environment in Pasuruan district, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 23(9), 4460–4465. Yanestria, S.M., Effendi, M.H., Tyasningsih, W., Moses, I.B., Khairullah, A.R., Kurniawan, S.C., Dameanti, F.N.A.E.P., Ikaratri, R., Pratama, J.W.A., Sigit, M., Hasib, A. and Silaen, O.S.M. 2024. Antimicrobial resistance patterns and genes of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from chickens in Pasuruan, Indonesia. Open Vet. J. 14(3), 759–768. Yopa, D.S., Massom, D.M., Kiki, G.M., Sophie, R.W., Fasine, S., Thiam, O., Zinaba, L. and Ngangue, P. 2023. Barriers and enablers to the implementation of one health strategies in developing countries: a systematic review. Front. Public Health 11(1), 1252428. | ||
| How to Cite this Article |
| Pubmed Style Thesia NLN, Khairullah AR, Effendi MH, Tyasningsih W, Puspitasari Y, Ahadini SN, Moses IB, Yanestria SM, Riwu KHP, Wasito W, Baihaqi ZA, Ahmad RZ. Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia. Open Vet. J.. 2025; 15(1): 300-306. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 Web Style Thesia NLN, Khairullah AR, Effendi MH, Tyasningsih W, Puspitasari Y, Ahadini SN, Moses IB, Yanestria SM, Riwu KHP, Wasito W, Baihaqi ZA, Ahmad RZ. Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia. https://www.openveterinaryjournal.com/?mno=224019 [Access: January 26, 2026]. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 AMA (American Medical Association) Style Thesia NLN, Khairullah AR, Effendi MH, Tyasningsih W, Puspitasari Y, Ahadini SN, Moses IB, Yanestria SM, Riwu KHP, Wasito W, Baihaqi ZA, Ahmad RZ. Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia. Open Vet. J.. 2025; 15(1): 300-306. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 Vancouver/ICMJE Style Thesia NLN, Khairullah AR, Effendi MH, Tyasningsih W, Puspitasari Y, Ahadini SN, Moses IB, Yanestria SM, Riwu KHP, Wasito W, Baihaqi ZA, Ahmad RZ. Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia. Open Vet. J.. (2025), [cited January 26, 2026]; 15(1): 300-306. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 Harvard Style Thesia, N. L. N., Khairullah, . A. R., Effendi, . M. H., Tyasningsih, . W., Puspitasari, . Y., Ahadini, . S. N., Moses, . I. B., Yanestria, . S. M., Riwu, . K. H. P., Wasito, . W., Baihaqi, . Z. A. & Ahmad, . R. Z. (2025) Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia. Open Vet. J., 15 (1), 300-306. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 Turabian Style Thesia, Naomi Lan Noviana, Aswin Rafif Khairullah, Mustofa Helmi Effendi, Wiwiek Tyasningsih, Yulianna Puspitasari, Susmitha Nur Ahadini, Ikechukwu Benjamin Moses, Sheila Marty Yanestria, Katty Hendriana Priscilia Riwu, Wasito Wasito, Zein Ahmad Baihaqi, and Riza Zainuddin Ahmad. 2025. Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia. Open Veterinary Journal, 15 (1), 300-306. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 Chicago Style Thesia, Naomi Lan Noviana, Aswin Rafif Khairullah, Mustofa Helmi Effendi, Wiwiek Tyasningsih, Yulianna Puspitasari, Susmitha Nur Ahadini, Ikechukwu Benjamin Moses, Sheila Marty Yanestria, Katty Hendriana Priscilia Riwu, Wasito Wasito, Zein Ahmad Baihaqi, and Riza Zainuddin Ahmad. "Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia." Open Veterinary Journal 15 (2025), 300-306. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 MLA (The Modern Language Association) Style Thesia, Naomi Lan Noviana, Aswin Rafif Khairullah, Mustofa Helmi Effendi, Wiwiek Tyasningsih, Yulianna Puspitasari, Susmitha Nur Ahadini, Ikechukwu Benjamin Moses, Sheila Marty Yanestria, Katty Hendriana Priscilia Riwu, Wasito Wasito, Zein Ahmad Baihaqi, and Riza Zainuddin Ahmad. "Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia." Open Veterinary Journal 15.1 (2025), 300-306. Print. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 APA (American Psychological Association) Style Thesia, N. L. N., Khairullah, . A. R., Effendi, . M. H., Tyasningsih, . W., Puspitasari, . Y., Ahadini, . S. N., Moses, . I. B., Yanestria, . S. M., Riwu, . K. H. P., Wasito, . W., Baihaqi, . Z. A. & Ahmad, . R. Z. (2025) Detection of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from duck cloacal swab in Jombang, Indonesia. Open Veterinary Journal, 15 (1), 300-306. doi:10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i1.28 |